This post may contain affiliate links which means as an Amazon Associate, this site may earn a small commission on qualified purchases made through links at no extra cost to you. Learn more on Affiliate Disclosure

Have you ever woken up to find small bites on your body, or noticed tiny bugs crawling around on your pillow or sheets? If so, you may be dealing with a bed bug infestation. However, while bed bugs are certainly a common pest that can cause sleepless nights and itchy bites, they are not the only tiny bugs that can infest your bed.
In fact, there are many different types of tiny bugs that can be found in your bed, each with its own unique characteristics and behaviors. From dust mites to carpet beetles, these tiny pests can cause a range of problems, from mild irritation to more severe allergic reactions.
In this article, we’ll explore 20 different types of tiny bugs that can infest your bed, and provide you with tips on how to identify and get rid of them. By learning about these common pests and taking steps to prevent and eliminate them, you can ensure that your bed is a clean, comfortable, and healthy place to sleep. So if you’re ready to say goodbye to tiny bugs in bed for good, keep reading!
What Are Tiny Bugs in Bed?
Tiny bugs in bed are a common problem that can cause discomfort and irritation for many people. They are typically small in size, ranging from a few millimeters to a few centimeters, and can be found in various parts of the bed, including the mattress, pillows, and bedding. These bugs are often mistaken for bed bugs, but they are actually a different type of insect altogether.
Some of the most common types of tiny bugs found in beds include booklice, carpet beetles, spider beetles, fleas, and dust mites. These bugs can cause a range of issues, including skin irritation, allergic reactions, and even respiratory problems.
Booklice are tiny insects that are commonly found in books and other paper products, but they can also infest bedding and other areas of the home. They are typically less than 1mm in size and are often mistaken for bed bug nymphs due to their similar appearance.
Carpet beetles are another common type of tiny bug found in beds. They are small, oval-shaped insects that are typically brown or black in color. They feed on a variety of organic materials, including carpet fibers, clothing, and bedding.
Spider beetles are similar in appearance to carpet beetles, but they have longer legs and more rounded bodies. They are also brown or black in color and can be found in various parts of the home, including bedding and clothing.
Fleas are tiny, wingless insects that are typically found on pets but can also infest bedding and other areas of the home. They can cause skin irritation and can also transmit diseases to humans.
Dust mites are microscopic insects that feed on dead skin cells and can be found in bedding, carpeting, and upholstered furniture. They are a common trigger for allergies and can cause respiratory issues for some people.
While tiny bugs in bed can be a nuisance, they are not usually a serious health threat. However, it is important to identify and address any infestations to prevent further issues and discomfort. In the following sections, we will explore some of the most common types of tiny bugs found in beds and how to get rid of them in detail.
Bed bugs
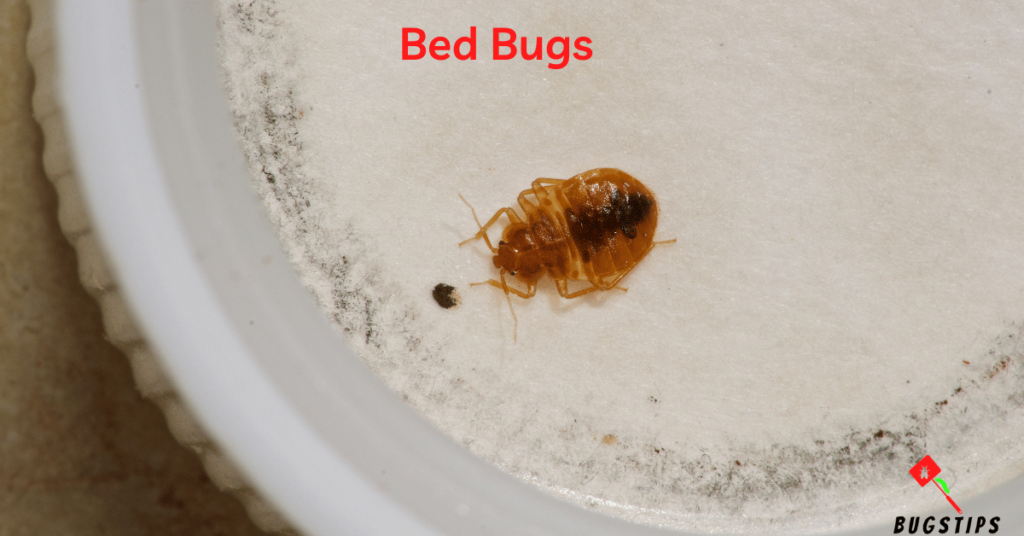

Tiny bugs in bed can be quite a nuisance and one of the most common ones is bed bugs.
Bed bugs are small, oval-shaped insects that are commonly found in bed frames, mattresses, and other furniture. They are about the size of an apple seed and are reddish-brown in color. Bed bugs are nocturnal and feed on the blood of humans and animals while they sleep.
If you suspect you have bed bugs in your home, it is important to take action immediately. Bed bugs can reproduce quickly and can spread throughout your home, making it difficult to eliminate them. By understanding the signs of a bed bug infestation and taking preventative measures, you can help protect yourself and your family from these tiny bugs in bed.
Identification
To identify bed bugs, you should look for the following signs:
- Small, reddish-brown bugs on your bed sheets, pillowcases, or mattress
- Dark spots or stains on your bedding, which are the bed bug’s excrement
- Small, whitish eggs or eggshells
- An unpleasant, sweet, musty odor in your bedroom
If you see any of these signs, you likely have a bed bug infestation.
Related Article – Baby Bed Bugs: 10 Facts You Need to See (with Pictures!)
How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs
Getting rid of bed bugs can be challenging, but there are several steps you can take to eliminate them:
- Wash all of your bedding, clothes, and curtains in hot water and dry them on high heat. This will kill any bed bugs and their eggs.
- Vacuum your mattress, bed frame, and surrounding areas thoroughly, including cracks and crevices. Make sure to dispose of the vacuum bag outside your home.
- Use bed bug mattress encasements to prevent bed bugs from getting in or out of your mattress.
- Seal up any cracks or crevices in your bedroom walls or furniture, as bed bugs can hide in these areas.
- Use insecticides or bed bug sprays, following the instructions carefully. It’s recommended to seek the help of a professional exterminator to ensure the complete elimination of the infestation.
Read More – How to Get Rid of Bed Bugs on Headboard
Remember to be vigilant and act quickly if you suspect a bed bug infestation, as they can quickly spread to other areas of your home.
Dust Mites
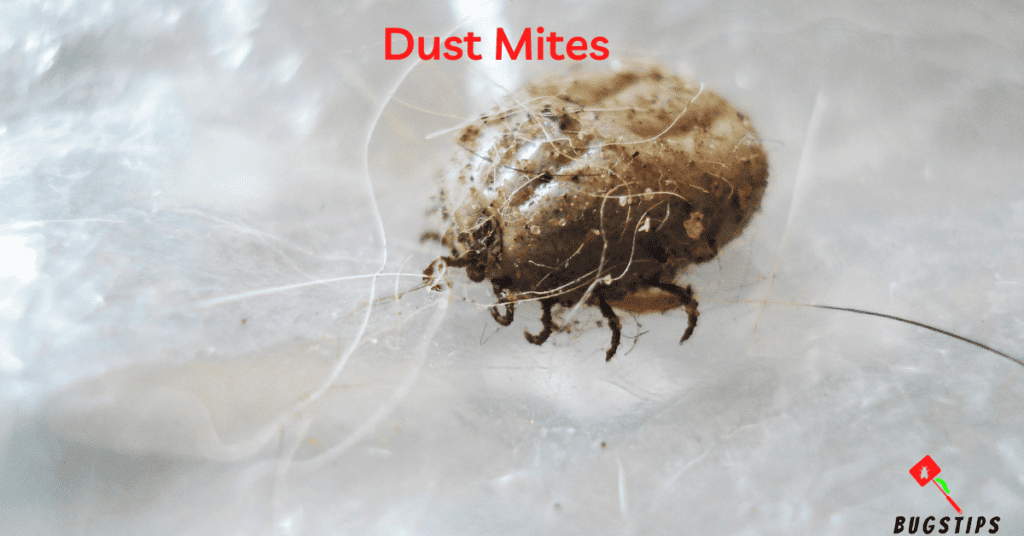

Dust mites are tiny arthropods that feed on dead skin cells shed by humans and pets. They thrive in warm and humid environments, making beds a perfect breeding ground. These microscopic bugs are virtually impossible to see with the naked eye, making it difficult to detect their presence. They can cause allergic reactions in some people, including sneezing, runny nose, and itchy eyes.
Dust mites are commonly found in bedding, mattresses, and carpets. They can also be found in upholstered furniture and stuffed animals. Although they do not bite or sting, their presence can cause discomfort for those with allergies. Regular cleaning of bedding and carpets, using dust-proof covers on mattresses and pillows, and washing bedding in hot water can help to reduce dust mite populations in the home.
Related Article – Bed Bugs vs Scabies – 5 Key Differences and Similarities
Identification
To identify dust mites, look for the following signs:
- Allergies: If you or anyone in your family has allergies or asthma, it is likely that dust mites are present in your home.
- Visible mites: Dust mites are not visible to the naked eye, but they can be seen under a microscope.
- Shed skin and fecal matter: Dust mites shed their skin and leave behind fecal matter, which can be found in dust and on bedding.
- High humidity: Dust mites thrive in warm and humid environments, so high humidity levels in your home may indicate their presence.
- Visible symptoms: Symptoms such as itchy eyes, sneezing, or a runny nose may indicate the presence of dust mites in your home.
How to Get Rid of Dust Mites
- Wash bedding and linens in hot water and dry on high heat. This will kill dust mites and their eggs.
- Use allergen-proof covers for your mattress, box spring, and pillows to prevent dust mites from settling in.
- Vacuum your home frequently using a vacuum cleaner with a HEPA filter to trap small dust particles and mites.
- Dust surfaces in your home regularly with a damp cloth or microfiber cloth to prevent dust buildup.
- Keep humidity levels low in your home, ideally between 30-50%. You can use a dehumidifier to achieve this.
- Use an air purifier with a HEPA filter to remove dust and other allergens from the air.
- Replace carpets with hard flooring or low-pile carpeting, as carpets can trap dust and mites.
- Clean or replace air filters in your home’s heating and cooling system regularly.
By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the number of dust mites in your home and alleviate any allergy symptoms caused by them.
Fleas
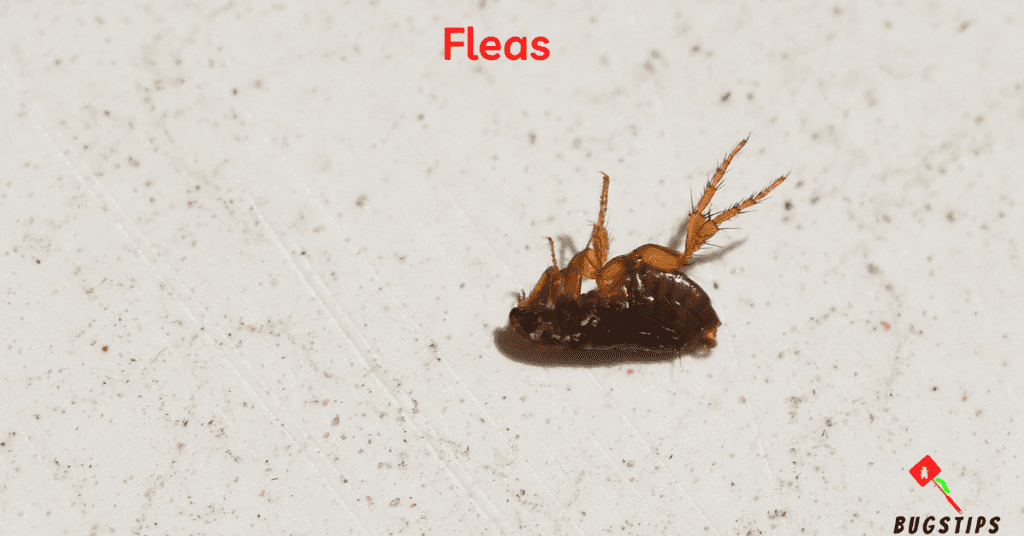

Fleas are small, wingless insects that feed on the blood of mammals and birds. They are about 1/8 inch in length and are typically brown or reddish-brown in color. Fleas are commonly associated with pets, but they can also infest human living spaces. Fleas are known to jump long distances and are often able to move from one host to another with ease. They are most active during warm and humid weather, and their populations tend to increase during the summer months.
Flea bites can cause itching, redness, and irritation on the skin. In addition to being a nuisance, fleas can also transmit diseases to humans and animals. Some of the diseases that can be transmitted by fleas include typhus, plague, and cat scratch fever. It is important to take preventative measures to avoid flea infestations in the home, such as regularly washing bedding and vacuuming carpets and furniture. If a flea infestation is suspected, it is important to seek professional pest control services to effectively eliminate the infestation.
Identification
- Look for small, reddish-brown bugs that are about 1/8 inch long and have flat bodies
- Check your pets for signs of fleas, such as excessive scratching, flea dirt (small black specks that are actually flea feces), or small red bumps on their skin
- Look for flea bites on yourself, which appear as small, red, itchy bumps on the skin
How to Get Rid of Fleas
- Treat Your Pets:
- Give your pets a flea bath or use a flea treatment recommended by your veterinarian
- Use flea combs to remove any remaining fleas and their eggs from your pet’s fur
- Keep your pets away from areas where fleas are likely to live, such as tall grass or wooded areas
- Clean Your Home:
- Vacuum your floors, carpets, and furniture regularly, and dispose of the vacuum bag outside your home
- Wash your pet’s bedding, toys, and other items in hot water and dry them on high heat
- Use a flea spray or fogger in your home, following the instructions carefully
- Seal up any cracks or crevices in your home where fleas can hide, such as baseboards or gaps in the floorboards
- Treat Your Yard:
- Keep your yard well-manicured and remove any debris or piles of leaves or grass
- Use an insecticide or flea repellent in your yard, following the instructions carefully
- Keep your pets away from areas where fleas are likely to live, such as tall grass or wooded areas
Remember to be persistent in your efforts to get rid of fleas, as they can be difficult to eliminate completely. It may take several treatments and thorough cleaning to completely eradicate a flea infestation.
Ticks
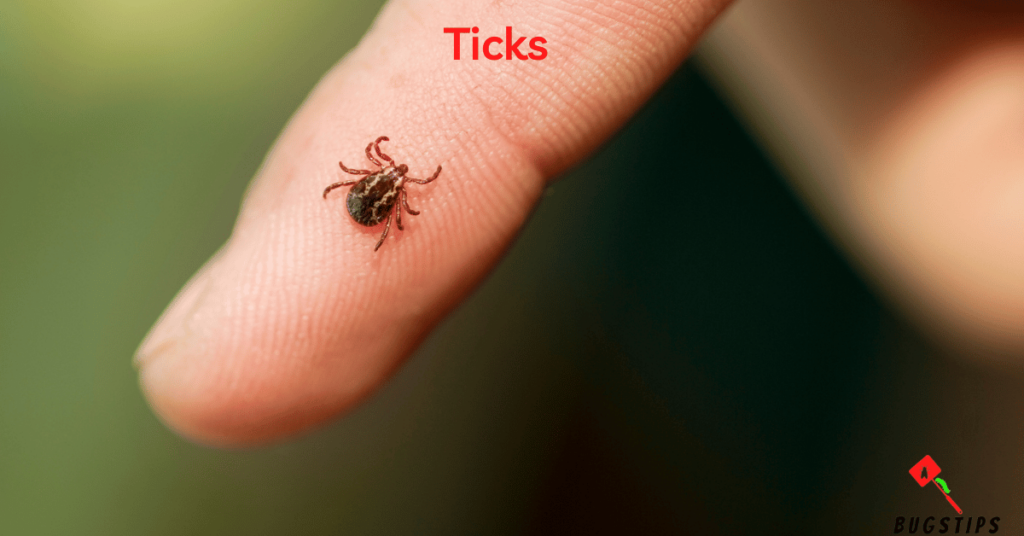

Ticks are tiny bugs in bed that are known to cause a range of health problems. These blood-sucking arachnids are common in outdoor environments such as forests, grassy areas, and gardens. However, ticks can also find their way into homes and settle into bedding, furniture, and carpeting. Identifying ticks can be tricky since they range in size from as small as a poppy seed to as large as a pencil eraser. Most ticks have a flattened, oval-shaped body and four pairs of legs. Their color can vary depending on the species and the stage of their life cycle.
Ticks can be carriers of various diseases, such as Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and babesiosis, among others. The symptoms of these diseases can be severe, and in some cases, life-threatening. It’s important to be aware of the potential risks of tick bites and take appropriate precautions when spending time outdoors. Checking your clothing, body, and bedding regularly for ticks is one way to minimize your exposure to these tiny bugs in bed.
Identification
- Ticks are small, flat, oval-shaped insects that are typically brown or black in color.
- They have eight legs and are about the size of a sesame seed.
- Ticks attach themselves to their host’s skin to feed on their blood.
How to Get Rid of Ticks
- Wear protective clothing: When outdoors in areas with tick populations, wear long-sleeved shirts, pants, and closed-toe shoes. Tuck pant legs into socks or boots, and consider wearing a hat and gloves.
- Use tick repellent: Use an EPA-registered insect repellent that contains at least 20% DEET, picaridin, or IR3535 on exposed skin and clothing. Always follow the instructions on the label.
- Check your body: After being outdoors, check your body for ticks. Pay special attention to areas such as the scalp, behind the ears, inside the belly button, around the waistband, and in the armpits and groin area.
- Remove ticks promptly: If you find a tick, remove it as soon as possible using fine-tipped tweezers. Grasp the tick as close to the skin’s surface as possible and pull upward with steady, even pressure. Do not twist or jerk the tick, as this can cause the mouthparts to break off and remain in the skin.
- Treat your pets: Talk to your veterinarian about the best tick prevention methods for your pets. Keep them away from tick-infested areas, and check them regularly for ticks.
- Manage your yard: Keep your lawn mowed and remove leaf litter, brush, and weeds around your home and in your yard. Consider using an insecticide or tick repellent in areas where ticks are likely to live, such as wooded or grassy areas.
- Consult a professional: If you are experiencing a severe tick infestation, it may be necessary to consult a pest control professional for assistance in eliminating the problem.
By following these steps, you can help protect yourself and your pets from ticks and reduce the risk of tick-borne illnesses.
Carpet Beetles
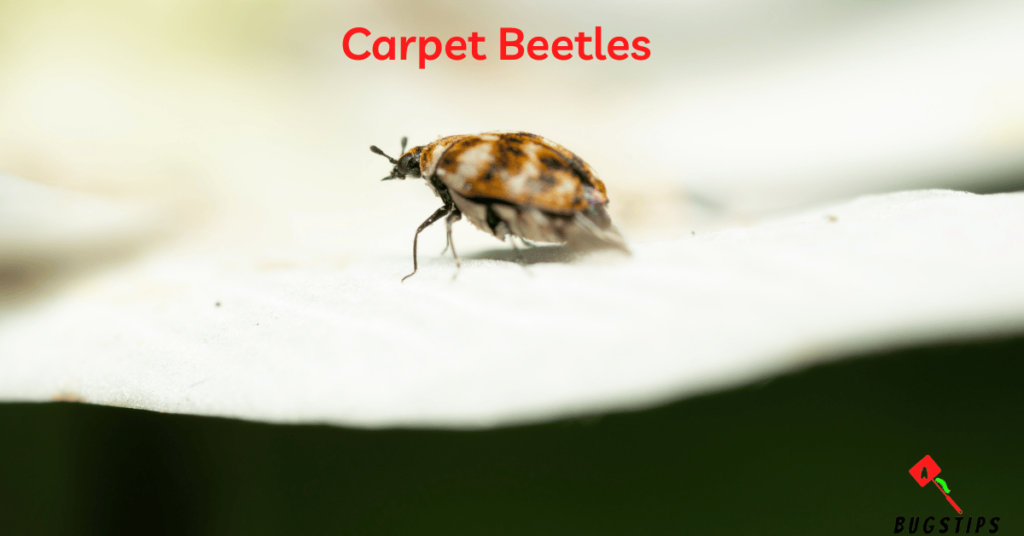

Carpet beetles are another common type of tiny bug that can be found in our homes, including beds. They are small and oval-shaped, with a varied pattern of white, brown, and black scales on their bodies. Carpet beetle larvae are covered in bristly hairs and can be mistaken for small, hairy worms. These insects feed on a wide range of organic materials, including wool, fur, feathers, and even dead insects, making our beds a suitable environment for them to thrive in.
Carpet beetles can cause damage to our bedding and clothing, but they do not pose a threat to health. However, their presence can be a nuisance and cause irritation to some people who are sensitive to their bristly hairs. Regular cleaning and vacuuming of bedding, carpets, and clothing can help prevent carpet beetle infestations. It is also important to store our clothing and bedding in airtight containers to reduce the risk of infestation.
Identification
- Look for small, oval-shaped beetles that are approximately 1/8 to 3/16 inch long and have a mottled pattern of white, brown, and black scales on their backs
- Check for shed skins or larvae, which are usually covered in small, hair-like bristles and can be found in the same areas as adult beetles
- Look for damage to fabrics or carpets, including small holes or irregular patterns of damage
How to Get Rid of Carpet Beetles
- Vacuum regularly: Regular vacuuming can help to remove adult beetles and their larvae from carpets, furniture, and other fabrics in your home. Be sure to vacuum thoroughly and dispose of the vacuum bag outside of your home.
- Clean and declutter: Carpet beetles are attracted to dust, debris, and clutter, so it’s important to keep your home clean and free of unnecessary items. Pay special attention to areas where natural fibers are stored or used, such as closets and storage areas.
- Use insecticides: There are several insecticides available that can help to kill carpet beetles and their larvae. Be sure to follow the instructions carefully and use protective gear, such as gloves and a mask, when applying insecticides.
- Freeze-infested items: If you have items that are infested with carpet beetle larvae, such as clothing or linens, you can place them in a plastic bag and freeze them for several days. This will kill the larvae and prevent further damage.
- Consult a professional: If you have a severe carpet beetle infestation, or if you are unsure of how to properly get rid of them, it is recommended to consult a pest control professional. They can provide effective treatment options and help prevent future infestations.
If you suspect that you have a carpet beetle infestation, it is important to take action as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your belongings.
Spider Beetles
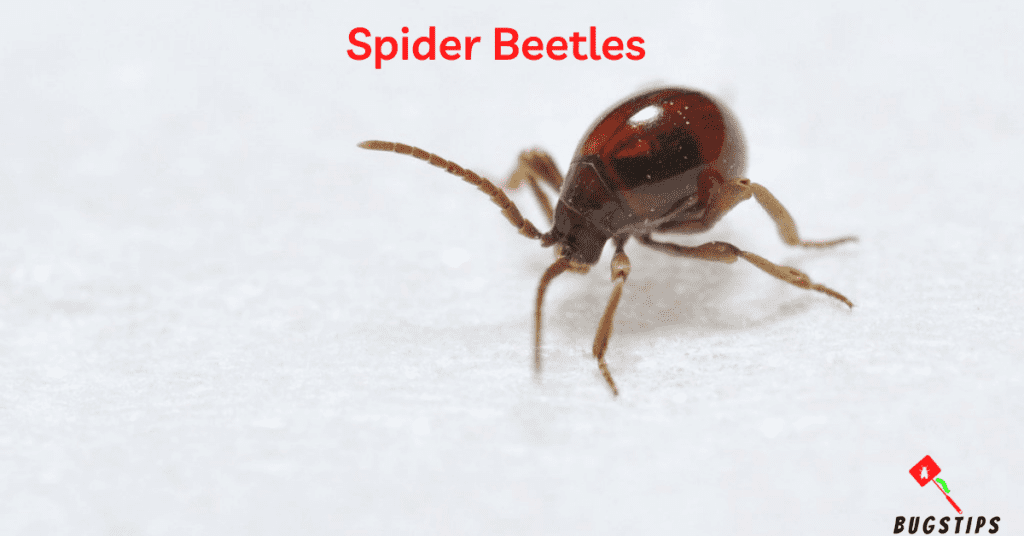

Spider beetles are a type of household pest that is commonly found in stored food products such as grains, cereals, and spices. These small, oval-shaped beetles are usually brown or black in color and have a distinctive spider-like appearance due to their long, thin legs. Unlike actual spiders, however, spider beetles do not spin webs and are not venomous.
While spider beetles are not known to cause any significant damage to human health, they can be a nuisance when they infest stored food items in your pantry or kitchen. The presence of spider beetles in your home may also indicate a larger pest problem, as they are known to feed on dead insects and animal carcasses as well.
Identification
- Spider beetles are small, brown, or reddish-brown beetles with round bodies and long legs that resemble spider’s legs.
- They are typically 1-4 mm in length and have two bulging eyes and a pointed head.
- Spider beetles are often found in stored food products, as well as in bird or rodent nests, and can infest carpets, furniture, and clothing.
How to Get Rid of Spider Beetles
- Identify and eliminate the source of infestation: Check for any stored food products that may be infested and dispose of them properly.
- Clean thoroughly: Vacuum carpets, furniture, and clothing to remove any spider beetles, larvae, or eggs. Be sure to dispose of the vacuum bag outside of the home.
- Use a residual insecticide: Apply an insecticide specifically labeled for spider beetles to infested areas, following the instructions carefully.
- Seal up cracks and crevices: Spider beetles can enter your home through small cracks or gaps in walls, floors, and ceilings. Seal these up to prevent future infestations.
- Monitor for re-infestation: Continue to monitor the infested areas for signs of spider beetles and re-treat as necessary.
If the infestation is severe or persistent, it may be necessary to consult a professional pest control service.
Booklice
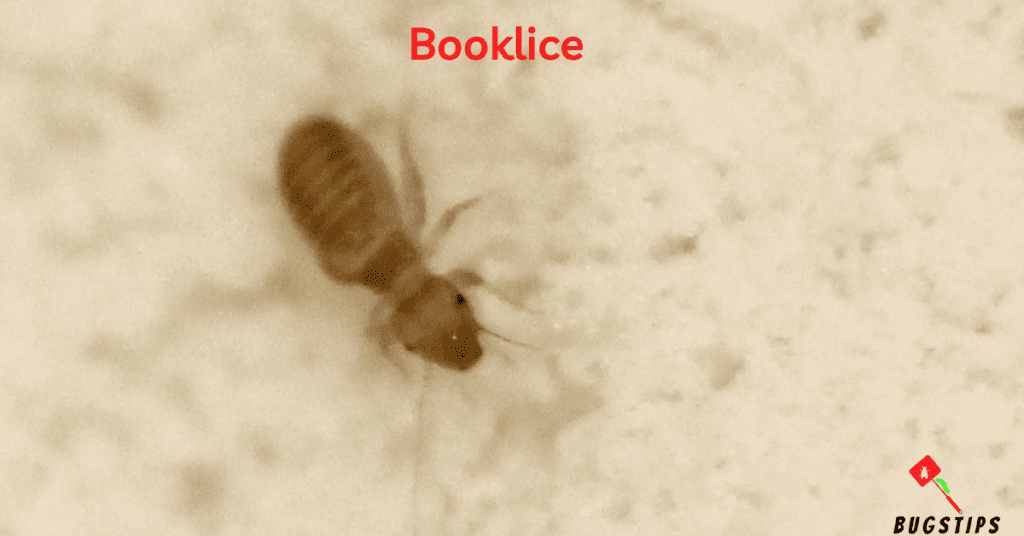

Booklice are tiny insects that are often found in humid environments, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and basements. Despite their name, they do not actually feed on books or paper products. Instead, they feed on mold and mildew, which can often be found in these damp areas. They are also attracted to starchy materials like flour and cereal, making them a common pantry pest.
Although booklice do not bite humans or cause any health issues, they can be a nuisance if they infest your home. They can quickly multiply and create an unsightly mess in food storage areas. It is important to keep your home dry and clean to prevent booklice infestations. Proper ventilation and dehumidification can help control the humidity in your home and prevent mold growth, which can attract booklice. Regular cleaning of food storage areas can also help prevent infestations by removing any food debris that may attract them.
Identification
- Look for small, gray, or brown insects that are less than 1/16 of an inch long
- Check for them in damp or humid areas of your home, such as basements, bathrooms, and kitchens
- Look for them near sources of moisture, such as leaky pipes or wet towels
How to Get Rid of Booklice
- Reduce humidity levels in your home by using a dehumidifier or air conditioner
- Repair any leaks or water damage in your home to eliminate sources of moisture
- Store food items in airtight containers to prevent booklice from infesting them
- Clean regularly to remove any dust or debris that may attract booklice
- Vacuum thoroughly, paying special attention to areas where booklice are present
- Use insecticides or natural remedies, such as diatomaceous earth or essential oils, to kill booklice and prevent future infestations
- Consider calling a professional pest control service if the infestation is severe or persistent.
It’s important to note that booklice do not bite or cause any damage to structures or materials in the home. However, they can be a nuisance and their presence may indicate a moisture problem in your home that needs to be addressed.
Cockroach Nymphs
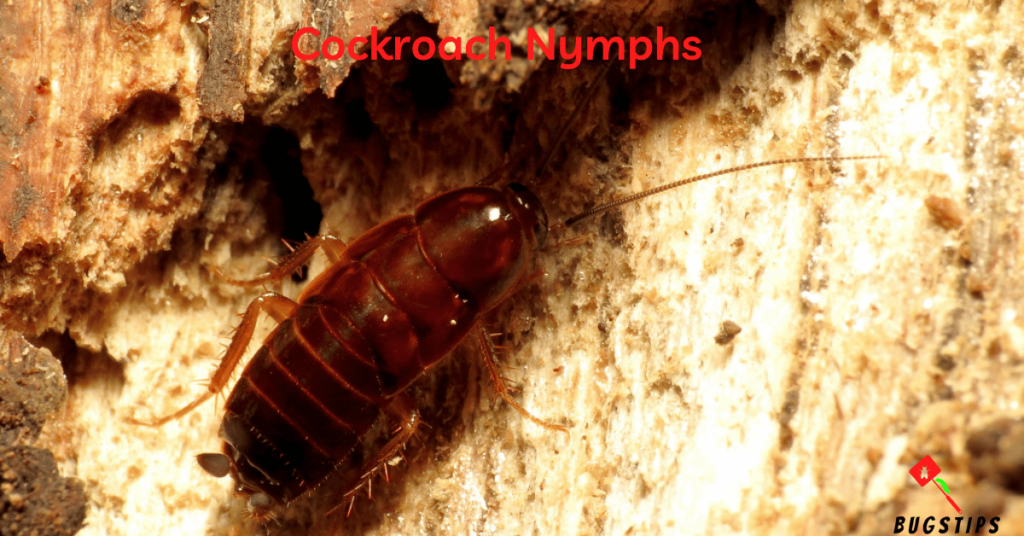

Cockroach nymphs are the immature stages of cockroaches and are often found in areas where cockroaches are present, including in and around homes. These tiny bugs can range in size from 1/16 to 3/4 of an inch, depending on their age and species. They are typically brown or black in color and have a flattened, elongated body shape.
Cockroach nymphs are known to be scavengers and can feed on a variety of organic matter, including food crumbs, grease, and even fecal matter. They are attracted to warm and humid environments, making bedrooms and other areas of the home with similar conditions a potential breeding ground for these tiny pests. While cockroach nymphs are not a direct threat to human health, they can trigger allergies and asthma in some individuals, and their presence can indicate a larger cockroach infestation in the home.
Identification
- Look for small, light-colored insects with similar body shapes and features as adult cockroaches
- Check-in areas where cockroaches are commonly found, such as kitchens, bathrooms, and basements
- Look for shed skins or egg casings, which can indicate the presence of nymphs
How to Get Rid of Cockroach Nymphs
- The first step in getting rid of cockroach nymphs is to identify and eliminate any sources of food or water that may be attracting them.
- This could involve fixing leaky pipes, sealing up cracks and crevices, and storing food in airtight containers.
- Insecticides can also be effective in controlling cockroach nymphs, but it is important to follow the instructions carefully and take safety precautions.
- Sticky traps or baits can also be used to catch and kill cockroach nymphs, but these may not be as effective as other methods.
- In severe infestations, it may be necessary to call in a professional pest control company to get rid of the cockroach nymphs.
Remember, eliminating cockroach nymphs can be a difficult and ongoing process. It’s important to be persistent and consistent with your efforts to prevent and control infestations.
Swallow Bugs
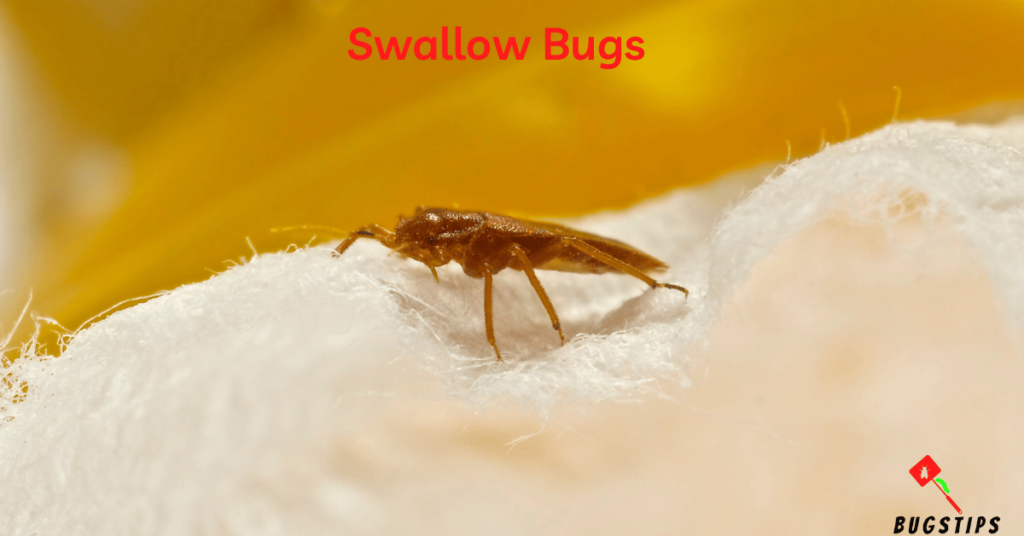

Swallow bugs, also known as bird bugs, are tiny insects that feed on the blood of birds and can infest homes that have nests nearby. Although they are not common household pests, they can become a nuisance if bird nests are located close to the house. These bugs are most active at night and can be found in areas such as bedrooms, closets, and attics. They are about the size of a grain of rice and are reddish-brown in color.
Swallow bugs can be easily mistaken for bed bugs due to their similar appearance and behavior. However, swallow bugs are typically found near bird nests and droppings, while bed bugs are commonly found in mattresses and bedding. Swallow bugs can also leave behind itchy bite marks on humans, but they do not infest humans or feed on human blood.
Identification
- Swallow bugs are about 1/4 inch long and are dark brown to black in color
- They have flat, oval-shaped bodies with short wings that do not allow them to fly
- Swallow bugs resemble bed bugs in appearance, but are typically larger and have long hairs on their legs and body
How to Get Rid of Swallow Bugs
- Locate the areas where swallow bugs are present and clean them thoroughly, removing any bird nests, droppings, or debris
- Seal any cracks or crevices in the walls, roof, or foundation of the structure to prevent swallow bugs from entering
- Use insecticides that are labeled for use against swallow bugs, following the instructions carefully
- Vacuum the affected area, including cracks and crevices, to remove any swallow bugs and their eggs
- Consider using diatomaceous earth, a natural insecticide that can be applied to cracks and crevices to kill swallow bugs
It is important to note that swallow bugs are primarily a pest for birds and are not typically known to infest human living spaces. However, if you have a pet bird or live near nesting sites, it is possible for these bugs to find their way into your home and bite humans during the night. If you suspect you have a swallow bug infestation, it is important to thoroughly inspect your home and take the necessary steps to eliminate the problem, as well as address any underlying bird-related issues that may be contributing to the infestation.
Head Lice
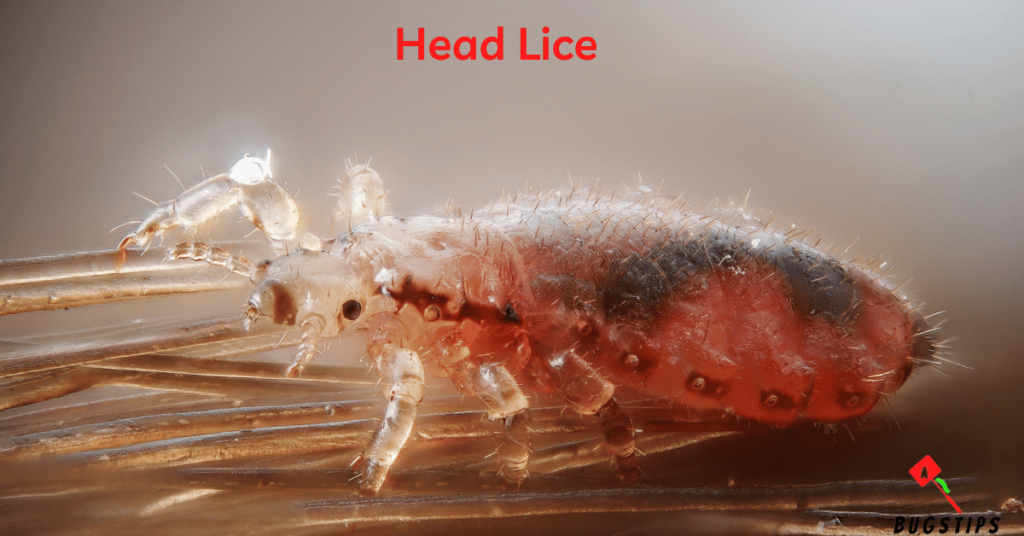

Head lice are tiny, wingless insects that live in human hair and feed on blood from the scalp. They are most common among school-age children and can easily spread through close personal contact or sharing of personal items such as combs or hats. However, it is possible for head lice to fall off the scalp and onto bedding or furniture, leading to the mistaken belief that they are tiny bugs in bed.
It’s important to note that head lice do not infest the home environment and cannot survive for more than a day or two without a human host. While it’s possible for lice to be transferred from one person to another through shared bedding or furniture, the risk of infestation in this way is relatively low. Despite their name, head lice can also be found on eyebrows and eyelashes.
Identification
- Presence of eggs, called nits, attached to hair shafts close to the scalp
- Adult lice, which are about the size of a sesame seed and can range in color from grayish-white to reddish-brown
- Itchy scalp and neck
How to Get Rid of Head Lice
- Use an over-the-counter (OTC) lice treatment shampoo or lotion as directed. Make sure to use a fine-toothed comb to remove dead lice and nits from the hair.
- Wash all clothing, bedding, and towels used in the past 2 days in hot water and dry on high heat for at least 20 minutes.
- Vacuum carpets, upholstery, and car seats, and dispose of the vacuum bag or empty the canister in a sealed bag.
- Soak combs and brushes in hot water for at least 10 minutes.
- Avoid sharing personal items such as hats, combs, and brushes.
It is important to follow the instructions carefully and repeat the treatment as directed to ensure the complete removal of head lice. In some cases, prescription medication may be necessary if OTC treatments are not effective.
Mites (including rat and bird mites)
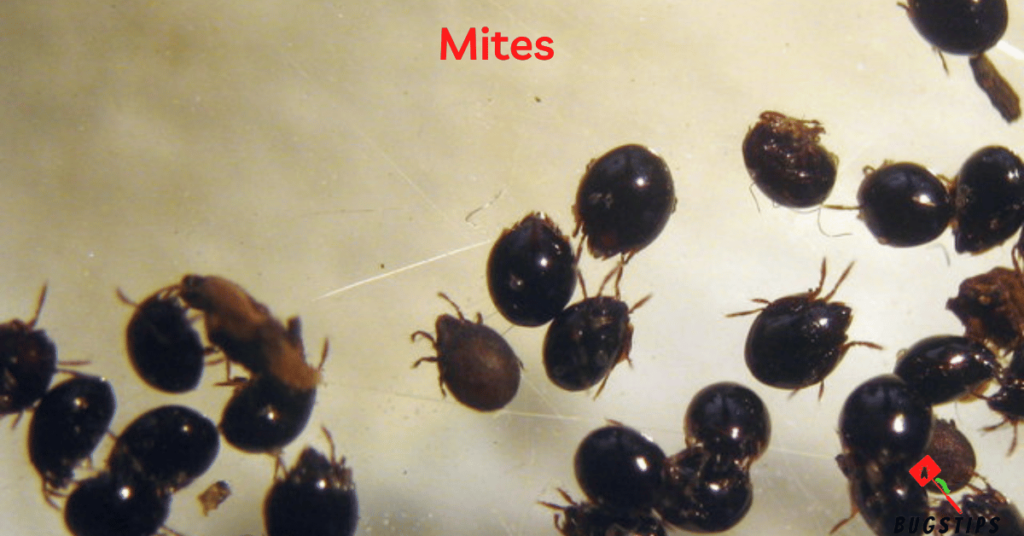

Mites are tiny, eight-legged arthropods that are commonly found in human living spaces. There are several types of mites, including rat mites and bird mites, which can be particularly troublesome for homeowners. These pests are known to feed on blood and can cause itchy bites and skin irritation.
Rat mites and bird mites are often found in homes when their hosts (rats or birds) are no longer present. Without a host to feed on, these mites will often seek out other sources of food, including humans. While they do not typically infest human living spaces, they can still be a nuisance and can cause health issues for those with allergies or weakened immune systems.
Identification
- Rat mites are usually pale in color and are smaller than other types of mites, measuring about 0.3 mm in length.
- Bird mites are usually dark in color and measure about 0.75 mm in length.
- Both types of mites can often be found in areas where rats or birds have been present, such as attics, crawl spaces, and wall voids.
How to Get Rid of Mites
- Vacuum regularly: Regular vacuuming can help remove mites from carpets, furniture, and bedding. Be sure to vacuum all areas thoroughly, including crevices and corners.
- Wash bedding and clothing: Wash all bedding and clothing in hot water to kill any mites that may be present. Use a dryer on high heat to further eliminate them.
- Use acaricides: Acaricides are chemical treatments that are effective in killing mites. These can be applied directly to affected areas or used in fumigation treatments.
- Use diatomaceous earth: Diatomaceous earth is a natural substance that can be effective in killing mites. It is a fine powder that can be sprinkled on affected areas and left for several hours before vacuuming up.
- Seal up entry points: Mites can enter homes through small cracks and gaps. Sealing up entry points can help prevent them from entering in the first place.
- Professional pest control: If the infestation is severe or persistent, it may be necessary to call in a professional pest control service. They can provide more specialized treatments and help ensure the mites are completely eliminated.
Regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent infestations before they occur. If you suspect a mite infestation, it is important to take action quickly to prevent further spread and discomfort.
Termites
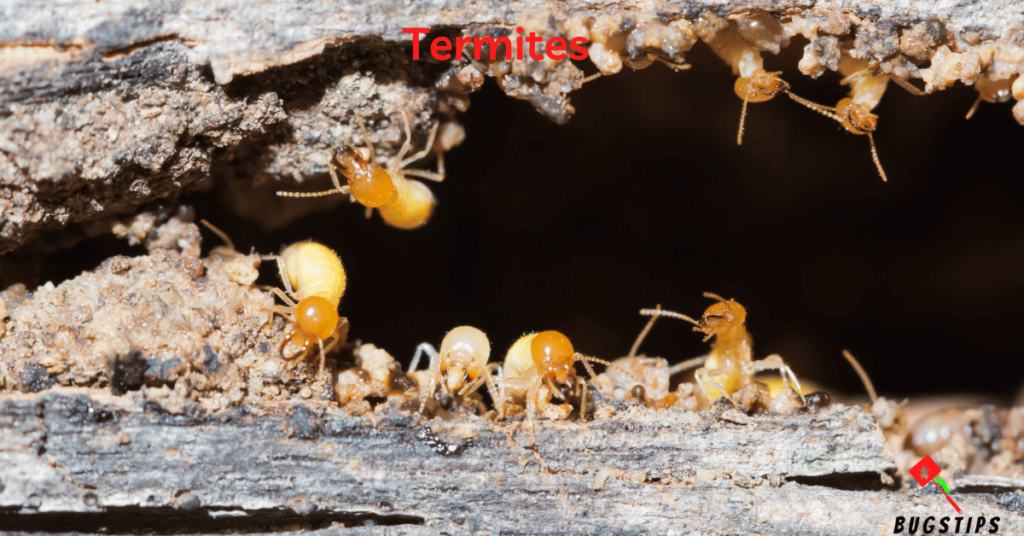

Termites are small, pale-colored insects that feed on wood and other cellulose-containing materials. They are known for causing significant damage to homes and other buildings, often without being detected until the damage is already done. While termites are not typically found in beds or bedding, it is still important to be aware of their presence in and around the home, as they can cause costly and extensive damage.
Some people may still encounter them in their sleeping areas. This could occur if there is termite damage to the structure of the home, allowing the termites to access the bedroom. It’s important to note that while termites do not pose a direct threat to human health, they can cause extensive damage to the structure of a home, including furniture and other wooden items.
Identification
- Termites are typically small, pale-colored insects, ranging in size from 1/8 inch to 1 inch in length.
- They have straight, beaded antennae and two pairs of wings that are equal in size and shape.
- Termites are often mistaken for ants but can be distinguished by their broad waist and straight antennae.
How to Get Rid of Termites
- Remove any infested wood or cellulose-containing materials from the home.
- Use bait stations or liquid termiticides to treat the soil around the home and prevent further infestations.
- Seal any cracks or openings in the home’s foundation to prevent termites from entering.
- Schedule regular termite inspections with a licensed pest control professional to detect and treat any infestations early.
termites are not typically found in beds or bedding. If you suspect a termite infestation in your home, it is best to contact a licensed pest control professional for proper identification and treatment.
Ants
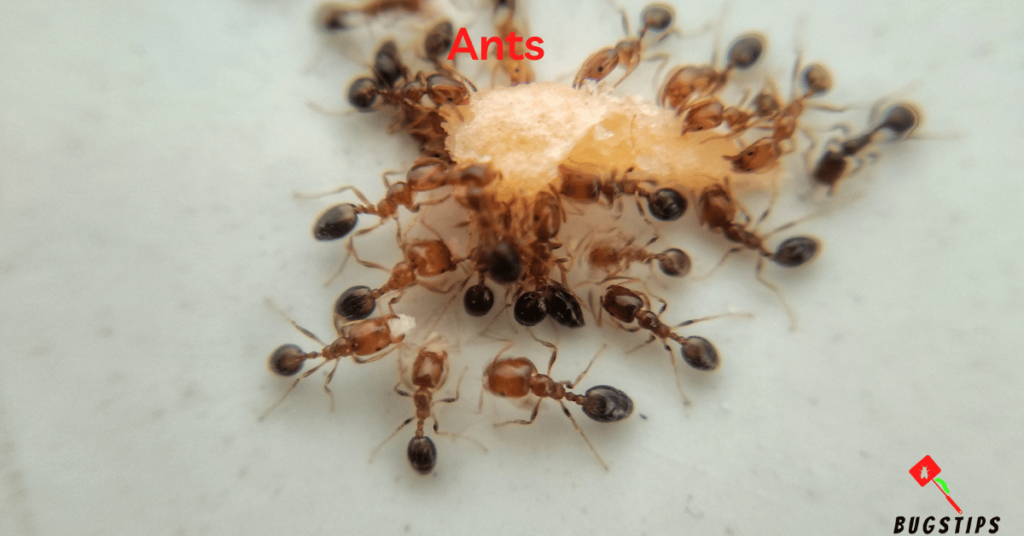

Ants are small, six-legged insects that can vary in color from red to black. While they are not typically known to infest beds or bedding, they can still be a nuisance and invade homes in search of food and water. Ants are attracted to a variety of foods, including sweets, meats, and fats, and can often be found in kitchens and pantries.
Related Article – What Chemicals Do Exterminators Use for Ants?
Ants typically enter homes through small cracks or openings and will leave behind a trail of pheromones for other ants to follow. While they are generally harmless to humans, large infestations can cause damage to structures and electrical systems. It is important to take measures to prevent ant infestations.
Identification
Identification of ants can be challenging since there are over 700 species of ants in the United States alone. However, some common signs that may indicate an ant infestation in your bed or bedroom include:
- Seeing ants crawling on or near your bed
- Finding ant trails leading to your bed or bedding
- Noticing small piles of dirt or debris near your bed, which could indicate ant nests
- Hearing rustling or scratching noises coming from your bed, which could indicate the presence of carpenter ants
How to Get Rid of Ants
- Identify the type of ant: Different species of ants may require different methods of elimination, so it’s important to identify the type of ant you are dealing with.
- Keep your bedroom clean: Ants are attracted to food crumbs and spills, so keeping your bedroom clean and free of crumbs and spills can help deter them.
- Use bait traps: Ant bait traps can be effective in attracting and killing ants. Place the traps near ant trails or suspected nesting sites.
- Seal entry points: Ants can enter your bedroom through tiny cracks and crevices, so seal any entry points to prevent them from getting in.
- Call a professional: If you have a persistent ant infestation that you can’t get rid of on your own, consider calling a pest control professional for assistance.
While ants in your bed can be a nuisance, they are not typically known to cause health problems. However, if you have an allergy to ant bites, their presence in your bed could be more problematic.
Spiders
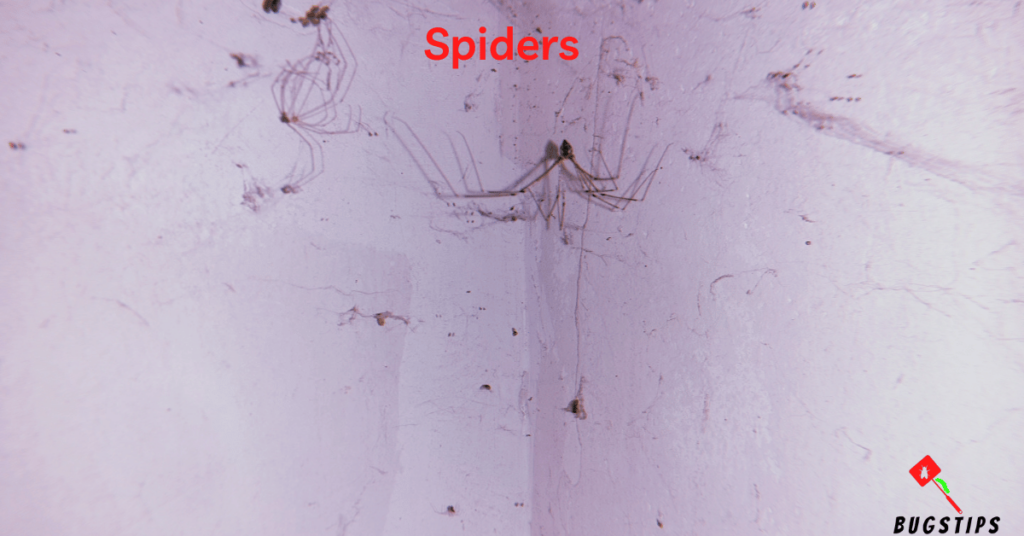

Spiders are arachnids that are often found in and around homes. While they are not typically considered a pest, some people may find them unsettling or even frightening if they encounter them in their beds or bedding. Spiders are attracted to warm and cozy places, which can include beds, especially if they are not frequently used. However, it is important to note that most spiders are harmless to humans and are actually beneficial because they help control other insect populations.
If you find a spider in your bed or bedding, it is important to remain calm and avoid disturbing it. While most spiders are harmless, some species can be venomous and should be avoided or removed by a professional.
Related Article – Can Spiders Bite Through Leggings, Socks, and Gloves? Find Out Here
Identification
- Look for the presence of webs in and around the bed area, as spiders often build their webs in quiet and undisturbed areas.
- Observe the physical characteristics of the spider, such as its size, color, and number of legs, to help identify the species of spider present in the bed area.
- Check for other signs of spider activity, such as spider egg sacs or shed skins.
How to Get Rid of Spiders
- Use a vacuum cleaner to remove spiders, webs, and egg sacs from the bed area.
- Seal up any cracks or gaps in the walls, windows, and doors to prevent spiders from entering the room.
- Keep the bed area free from clutter, as spiders often hide in piles of clothes or other items.
- Use spider repellents, such as essential oils or commercial insecticides, to deter spiders from the bed area.
- Keep the room well-ventilated and well-lit, as spiders prefer dark and damp areas.
Not all spiders are harmful or pose a threat to humans. In fact, most spiders are beneficial as they help control other insect populations. However, if you have a spider infestation in your bed area or if you’re allergic to spider bites, it’s best to seek professional help to safely remove them.
Weevils
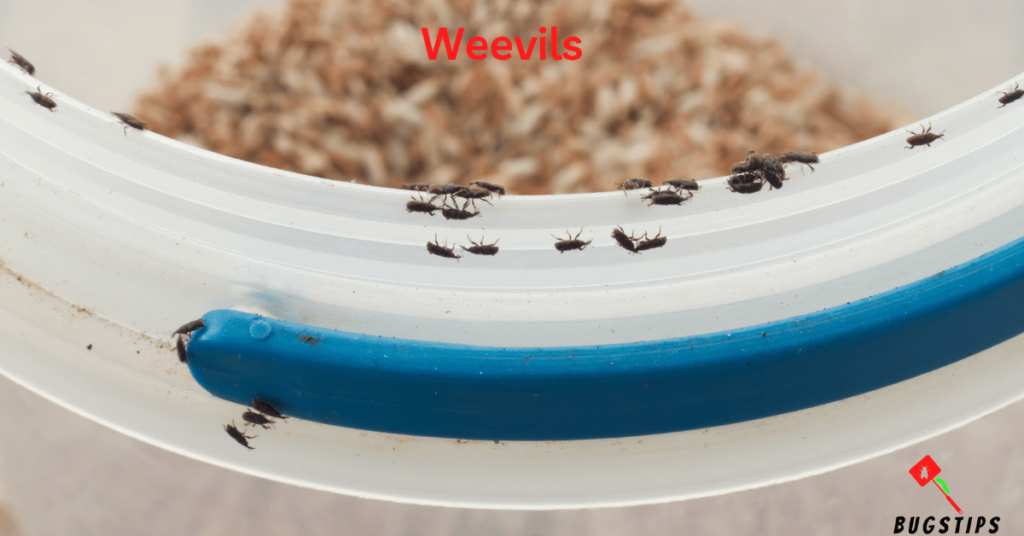

Weevils are small, beetle-like insects that are often found in grains, cereals, and other stored foods. While they may not typically be found in beds or bedding, it is important to be aware of their presence in the kitchen or pantry, as they can cause significant damage to food supplies. Weevils are attracted to grains, and can quickly spread throughout an entire pantry if not properly controlled.
In addition to their potential to damage food supplies, weevils can also be a nuisance when they start appearing in other areas of the home, such as bedrooms. They are often attracted to warmth and moisture and may find their way into beds and other soft materials. While they are not typically harmful to humans, their presence can be unpleasant and may indicate a larger infestation in the home.
Identification
- Weevils are small, dark-colored beetles with distinctive snouts on their head.
- They are typically found in stored food products, such as grains, nuts, and seeds.
- Weevils can also be found in bedding materials made from plant fibers, such as cotton and flax.
How to Get Rid of Weevils
- Locate the source of the infestation: Check all stored food products and bedding materials for signs of weevils, including adult beetles and larvae.
- Dispose of infested items: Discard any infested food products or bedding materials in a sealed plastic bag and dispose of them in an outdoor trash bin.
- Clean and vacuum: Thoroughly clean and vacuum all areas where weevils have been found, including pantry shelves, bedding, and carpeting.
- Store food properly: Store all food products in airtight containers to prevent weevils from getting in.
- Use natural repellents: Place bay leaves or whole cloves in your pantry and bedding areas as natural repellents. You can also use pheromone traps to capture adult weevils.
Weevils can be persistent and difficult to get rid of, so it may be necessary to repeat these steps multiple times to fully eliminate the infestation. Additionally, if the infestation is particularly severe, it may be necessary to call in a professional exterminator for assistance.
Springtails
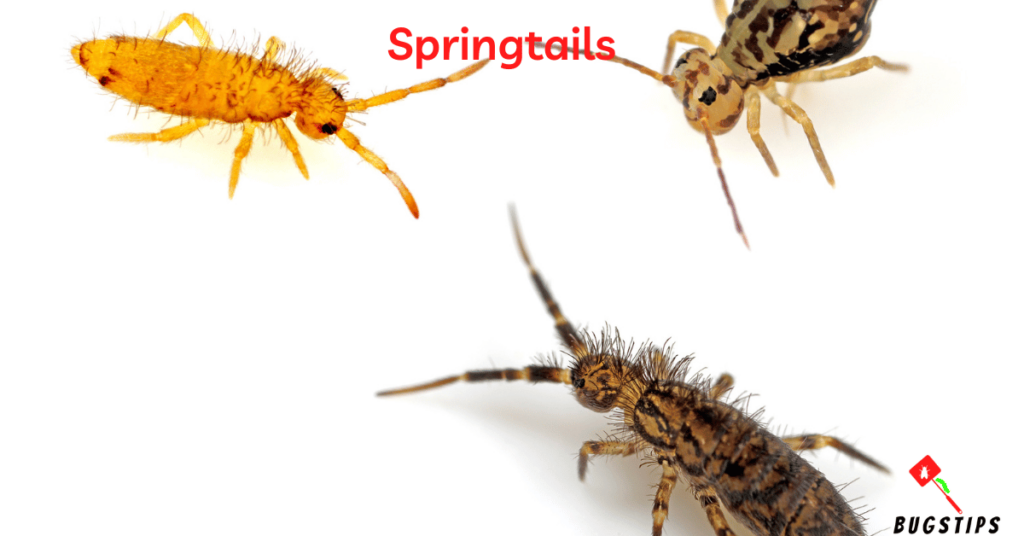

Springtails are tiny, wingless insects that are commonly found in damp soil, leaf litter, and other organic matter. They are known for their ability to jump considerable distances, using a specialized appendage called a furcula located on their abdomen. While they are not typically found in beds or bedding, they can occasionally be brought indoors on plants or in soil and may be found in damp areas of the home such as bathrooms or basements.
Springtails play an important role in the ecosystem, as they are important decomposers of organic matter and help to aerate the soil. They also serve as a food source for many other organisms, including some species of spiders and beetles. While they are generally considered to be harmless to humans, large populations of springtails can become a nuisance and may indicate underlying moisture or humidity issues in the home.
Identification
- Springtails are tiny, wingless insects that are typically only a few millimeters in length.
- They are usually black, white, or gray in color, and have a distinct ability to jump using a forked tail-like structure called a furcula.
- Springtails are commonly found in moist environments such as soil, leaf litter, and other decaying organic matter, but can sometimes be found in homes and even in bedding.
How to Get Rid of Springtails
- The best way to prevent springtails from entering your home and bedding is to eliminate excess moisture in your environment.
- Fix any leaks or areas of water accumulation, such as damp basements or bathrooms.
- Ensure proper ventilation and air circulation in your home to keep humidity levels low.
- If springtails have already infested your bedding or home, vacuuming and cleaning thoroughly can help remove them. It may also be necessary to use an insecticide specifically designed for springtails.
- If the infestation is severe, professional pest control services may be required to effectively eliminate the springtail population.
while springtails are not typically found in beds, it is important to be aware of their presence in and around the home. These tiny insects can be beneficial in breaking down organic matter in the soil but can become a nuisance when they invade indoor spaces. If you suspect an infestation or have concerns about the presence of any other tiny bugs in your bed or home, it is recommended to consult with a pest control professional for proper identification and treatment.
Stink Bug Nymphs
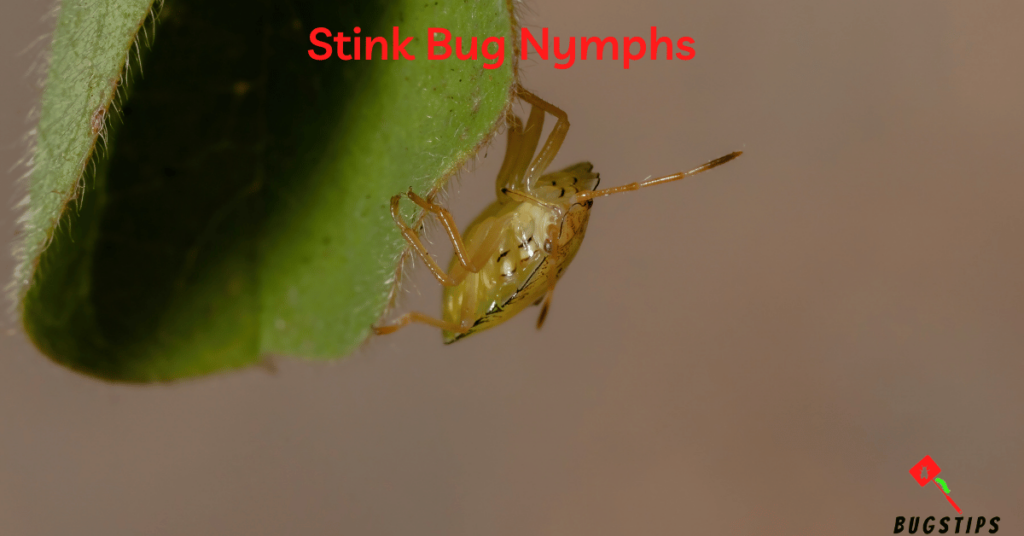

Stink bug nymphs are the immature form of stink bugs and are often smaller and more difficult to identify than adult stink bugs. These tiny bugs can sometimes find their way into beds or bedding, especially during the fall and winter months when they seek warmth indoors. While stink bug nymphs are generally harmless to humans, they can emit a foul odor if threatened or crushed, which can be unpleasant.
It is important to properly identify stink bug nymphs in order to distinguish them from other potential pests and to determine the best course of action for removal or prevention. Additionally, it is helpful to understand their behavior and habits in order to effectively control their presence in and around the home.
Identification
- Stink bug nymphs are small, wingless insects that resemble their adult counterparts, but are smaller and lack fully developed wings.
- They are typically a greenish or brownish color and have a distinctive shield-shaped body.
- Stink bug nymphs can sometimes be found in groups or clusters, especially on plants or other outdoor surfaces.
How to Get Rid of Stink Bug Nymphs
- The best way to prevent stink bug nymphs from entering the home is to seal all cracks and openings around windows, doors, and other entry points.
- If stink bug nymphs are already present in the home, they can be removed with a vacuum cleaner or by carefully capturing them with a tissue and disposing of them outside.
- It is important to avoid crushing or squishing stink bug nymphs, as they release a strong odor that can be unpleasant.
While stink bug nymphs may occasionally be found in beds, it is not a common occurrence. If stink bug nymphs are present in the bedroom, it is likely due to their proximity to an entry point or infestation in another area of the home.
No-see-ums ( Ceratopogonidae )
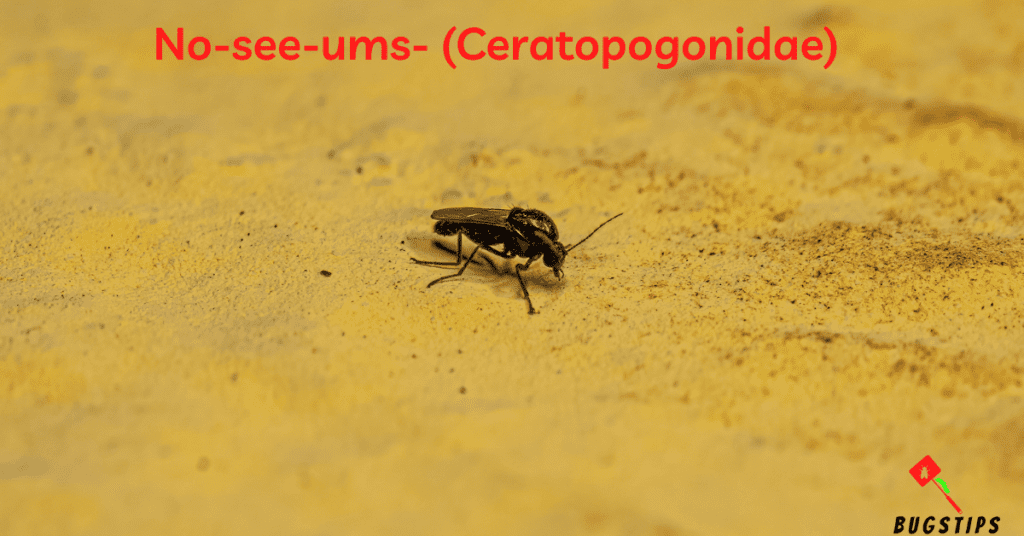

No-see-ums, also known as biting midges, are a type of tiny bug that can be found in and around the home. They are only 1-3 mm in size and can be difficult to spot. Despite their small size, they can deliver a painful bite and can be quite bothersome to humans and pets. No-see-ums are most active during dawn and dusk, making them particularly annoying during these times of the day. They can be found in a variety of habitats, including grassy areas, forests, and wetlands.
No-see-ums are known for their ability to breed in standing water, so it’s important to eliminate any sources of stagnant water around the home to prevent infestations. They can also be attracted to certain scents, such as perfumes and scented lotions, so it’s best to avoid using these products when spending time outdoors. No-see-ums can be difficult to control, but there are measures that can be taken to reduce their presence.
Identification
- No-see-ums are small, biting flies that belong to the family Ceratopogonidae. They are usually less than 1/8 inch in size and can be difficult to see with the naked eye.
- These tiny bugs are typically gray or black in color and have a humpbacked appearance.
- No-see-ums are most active at dawn and dusk, and their bites can be very itchy and painful.
How to Get Rid of No-see-ums
- One of the best ways to prevent no-see-ums from entering your home is by making sure all screens on doors and windows are in good condition and sealed tightly.
- If you do find no-see-ums in your home, vacuuming and sweeping regularly can help to eliminate them.
- You can also use insect repellent containing DEET to deter no-see-ums from biting you.
- In severe cases, a professional pest control service may be necessary to eliminate a no-see-um infestation.
While no-see-ums are tiny bugs that can be found in beds, they are not typically common household pests. However, if you do notice an infestation of no-see-ums in your home, it is important to take steps to eliminate them and prevent their return. With proper identification and a proactive approach to pest control, you can keep your home free from these pesky insects and enjoy a peaceful night’s sleep.
Bat Bugs

Bat bugs are small, flat, oval-shaped insects that are very similar in appearance to bed bugs. They are ectoparasites, meaning they feed on the blood of bats and can also bite humans. Bat bugs are commonly found in areas where bats roost, such as attics, chimneys, and other dark, secluded spaces. However, they can also be found in homes and can sometimes be carried into bedrooms or other living areas by bats or by people who have come into contact with infested materials.
Like bed bugs, bat bugs can be a nuisance to homeowners and can cause discomfort and irritation from their bites. While they are not known to transmit diseases to humans, their presence in the home can indicate the presence of a bat infestation, which can pose health risks to humans if left unaddressed. It is important to properly identify and address bat bug infestations in order to prevent further spread and potential health risks.
Identification
- Size: Adult bat bugs are about 3/16 inches (4-5 mm) long, while their nymphs are smaller (around 1.5 mm long).
- Color: They are reddish-brown to dark brown in color.
- Body shape: Oval and flattened body shape. Their heads are wider than their prothoraxes.
- Winged or wingless: Wingless bugs with reduced wings (wing pads) that do not overlap.
- Antennae: Their antennae have 4 segments with a distinct club on the last segment.
- Biting behavior: Bat bugs are blood-sucking insects that feed on the blood of bats and occasionally humans.
How to Get Rid of Bat Bugs
- Inspect and eliminate the source: If the bat bugs have invaded your home, it’s important to find and eliminate the source. This could be a bat colony or a previously infested structure nearby.
- Vacuum: Vacuuming can help remove any bat bugs, eggs, and droppings from affected areas, including carpets, cracks, and crevices.
- Launder-infested items: Infested bedding, clothing, and other washable items should be washed in hot water and dried on high heat to kill any bugs.
- Use insecticides: Insecticides, specifically labeled for bat bugs, can be used to treat cracks and crevices where bat bugs hide, such as baseboards, wall voids, and attics. It’s important to follow the label instructions and precautions when using any insecticides.
if you suspect you have bat bugs in your bed, it is important to take immediate action to address the infestation. Bat bugs can be difficult to get rid of on your own, so it may be necessary to seek professional pest control services. Additionally, it is important to ensure that any bat infestations in your home are also addressed to prevent the reinfestation of bat bugs. By taking these steps, you can eliminate bat bugs from your home and prevent any potential health risks associated with their presence.
Drugstore Beetles ( Bread Beetles )
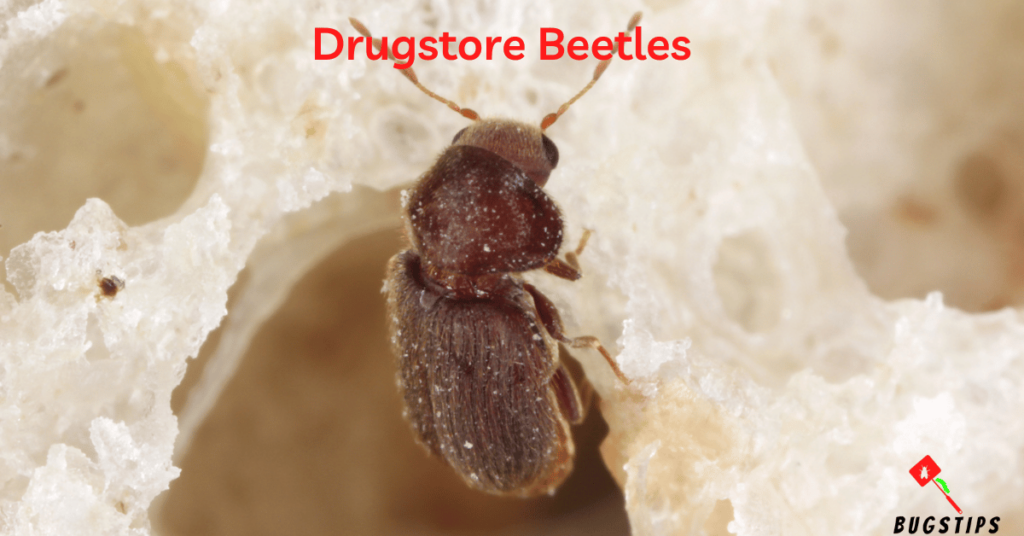

Drugstore beetles, also known as bread beetles, are small insects that can sometimes be found in beds. These beetles are commonly found in stored food products, such as grains, cereals, and spices, but they can also infest other organic materials such as books, wool, and silk. Drugstore beetles are oval-shaped, reddish-brown in color, and measure about 2-3 mm in length. While they do not bite or sting humans, they can cause damage to stored items and contaminate food products. If you suspect a drugstore beetle infestation in your home, it is important to take immediate action to prevent the infestation from spreading.
Identification
- Look for small, brownish beetles that measure around 1/8 inch in length.
- They have a distinct humpbacked shape and serrated antennae.
- Drugstore beetles can fly and are attracted to light.
- Check for holes or damage in stored food products, including grains, spices, and pet food.
- They can also infest non-food items like drugs, leather, and books.
How to Get Rid of Drugstore Beetles
- Locate the source of the infestation: Check all stored food items and packaging for signs of infestation. Dispose of any contaminated items immediately.
- Clean the affected area: Thoroughly vacuum the area where you found the beetles, including any cracks, crevices, and baseboards. Wipe down all surfaces with a cleaning solution to remove any potential food sources or eggs.
- Use insecticides: Apply an insecticide that is specifically labeled for drugstore beetles. Be sure to follow the instructions on the label carefully and take necessary precautions, such as wearing gloves and a mask.
- Contact a professional exterminator: If the infestation is severe or the beetles continue to reappear, it may be necessary to seek the assistance of a professional pest control company. They have the expertise and tools to effectively eradicate the infestation.
While Drugstore Beetles are tiny bugs commonly found in pantries and storage areas, they can also make their way into beds and cause irritation to humans. It is important to identify and eliminate these pests to prevent infestations in the home.
Common Misconceptions About Tiny Bugs in bed and Bed Bugs
There are several common misconceptions about tiny bugs in the bed, including bed bugs. One of the most prevalent misconceptions is that only dirty or unkempt homes have bed bugs. In reality, bed bugs can be found in any home regardless of cleanliness. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, which are present in every human dwelling.
Another misconception is that bed bugs are only found in beds. While they do prefer to feed on humans during sleep and are commonly found in mattresses and bedding, they can also be found in other furniture, carpeting, and even wall voids. This means that bed bugs can easily spread to other areas of a home or building, making them difficult to eliminate without professional pest control.
It’s also important to note that not all tiny bugs found in beds are bed bugs. As we’ve discussed earlier in this blog post, there are several other types of tiny bugs that can be found in bedding, such as dust mites and carpet beetles. It’s essential to correctly identify the pest in question before attempting to eliminate it, as different pests require different treatment methods.
Final Thoughts
Tiny bugs in bed can be a nuisance and cause discomfort to those affected by them. It is important to accurately identify these bugs to determine the best course of action for getting rid of them. Bed bugs are a common culprit, but it is important to be aware of other potential offenders such as springtails, stink bug nymphs, no-see-ums, and drugstore beetles.
By following the tips outlined in this article, such as maintaining a clean and clutter-free environment, regularly washing bedding and clothing, and properly sealing cracks and crevices, you can prevent and control the presence of these tiny bugs in your bed. We hope this comprehensive guide has provided you with valuable information to help you better understand and deal with the issue of tiny bugs in bed.
FAQ
Do bed bug bites look like tiny dots in a line?
Yes, bed bug bites can sometimes appear in a line or cluster of tiny dots on the skin. However, not all bed bug bites are in this pattern, and the appearance of bed bug bites can vary from person to person.
What bugs in bed are super tiny?
There are several bugs that can be found in beds that are very small, including dust mites, carpet beetles, and booklice. However, bed bugs are also small and are a common culprit of bed infestations.
Can you see bed mites?
Bed mites, or dust mites, are too small to be seen with the naked eye. They are about 0.3 millimeters in length and can only be seen under a microscope.
What is biting me in my bed that I can’t see?
There are several bugs that can bite humans while they sleep, including bed bugs, fleas, and mites. It is important to properly identify the bug in question to determine the best method of treatment.
Why do I feel bugs crawling on me in bed?
The sensation of bugs crawling on the skin while in bed can be caused by many factors, including anxiety, stress, or a medical condition. It is important to seek medical advice if the sensation persists or is accompanied by other symptoms.
Will bed bugs stay away if I keep the lights on?
No, bed bugs are not necessarily deterred by light. They are attracted to warmth and carbon dioxide, which are produced by humans and will infest areas where they have access to a host.
How can I prevent tiny bugs from getting into my bed?
To prevent tiny bugs from infesting your bed, it is important to regularly change and wash bedding in hot water, vacuum your bedroom frequently, and inspect second-hand furniture before bringing it into your home. Additionally, sealing cracks and crevices in walls and floors can help prevent bugs from entering the home.
Resources – (for further reading)
Mayo Clinic – Dust Mites
University of Kentucky – Bed Bugs and Other Household Pests
Colorado State University Extension – Bed Bug Lookalikes
Wikipedia – Drugstore Beetle
University of Minnesota Extension – Springtails