This post may contain affiliate links which means as an Amazon Associate, this site may earn a small commission on qualified purchases made through links at no extra cost to you. Learn more on Affiliate Disclosure
If you’re curious about moles and their vision, you might be wondering, “Do moles have eyes?” It’s a valid question, given that moles are known for their subterranean lifestyle and are rarely seen above ground.
In this article, we’ll explore the topic of moles and their eyesight and answer this question in detail. We’ll take a deep dive into how moles see, how they use their vision to navigate their environment, and why their eyes are an essential part of their biology.
So, if you’re interested in learning more about moles and their eyes, keep reading!
Do Moles Have Eyes?

Moles do have eyes, but they are not easily visible. Moles’ eyes are small and covered in fur, which makes them difficult to see. They are also positioned low on the head, which helps protect them from debris and dirt while the mole is digging.
Moles’ eyes are adapted to their subterranean lifestyle. Since moles spend most of their time underground, their eyes are not as important for vision as they are for sensing light.
Moles have very sensitive eyes that can detect even the slightest changes in light levels. This allows them to navigate their environment and detect predators or other potential dangers.
You May Also Like – Can Spiders See in the Dark? The Truthful Answer
The Anatomy of Moles’ Eyes
Moles are known for their subterranean lifestyle, spending most of their time tunneling underground in search of food and mates. As such, their eyes have evolved to suit their unique needs.
The eyes of common moles are small and difficult to see, measuring only about 1 mm in diameter. They are positioned low on the head and covered in fur, which helps protect them from dirt and debris while the mole is digging.
The eyelids of common moles are fused, which means that they cannot blink or close their eyes completely. Instead, they can only distinguish between light and dark.
Moles’ eyes are highly specialized for sensing light, allowing them to navigate their environment and detect potential threats. They lack external ears, which could fill up with dirt while tunneling.
Despite their small size and limited function, moles’ eyes are an essential part of their anatomy. They are equipped with a layer of tissue behind the retina called the tapetum lucidum, which reflects light through the retina to enhance their vision in low-light conditions.
Additionally, moles have a high number of rod cells in their eyes, which are specialized cells that are sensitive to light and help them detect even the slightest changes in light levels.
Related Article – Skunk Holes | The Comprehensive Guide
How Do Moles Use Their Eyes?
While moles’ eyes may not be their primary sense, they still serve important purposes in their underground world. Here are how moles utilize their eyes in their unique lifestyle.
- Moles use their eyes primarily to detect light and shadows, which helps them navigate their underground environment.
- While moles can distinguish between light and dark, they cannot see colors or fine details.
- Moles use their eyes to detect potential threats, such as predators, and avoid danger.
- Their eyes are highly sensitive to changes in light levels, allowing them to detect even the slightest movements or changes in light.
- Moles use their eyes to find their way around their tunnels and locate food sources.
- Their eyes help them to navigate the twists and turns of their tunnels and to avoid obstacles.
What Senses Do Moles Use Besides Eyesight?
In addition to their eyesight, moles rely on a variety of other senses to successfully navigate their underground environment and locate food.
Here are some of the senses that moles use besides their eyesight.
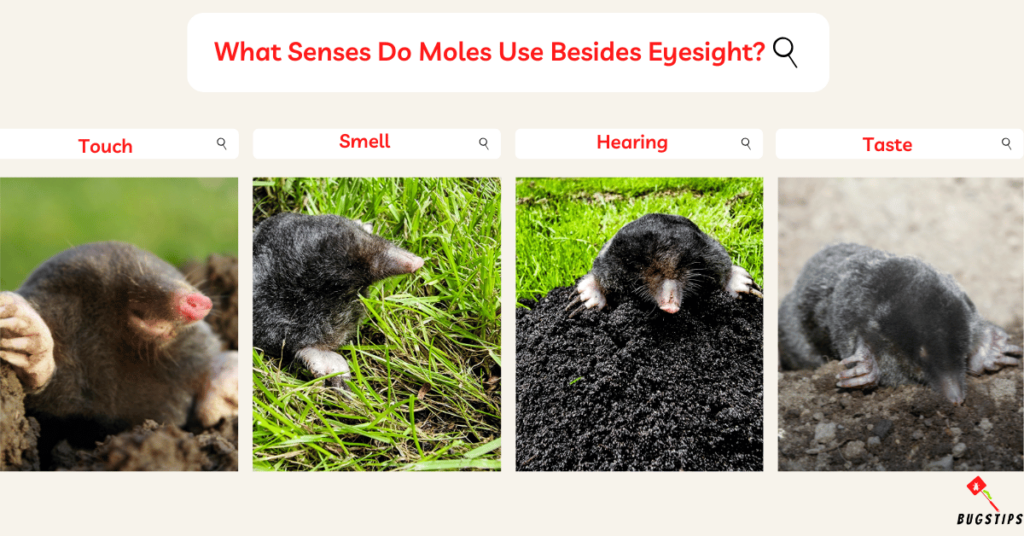
Touch
- Moles have a highly developed sense of touch, which serves as their primary sense.
- This sense allows them to feel their way through the soil, detecting changes in texture and consistency as they burrow.
- Their front paws are large and strong, and they use them to dig tunnels, find food, and avoid obstacles.
Smell
- Moles have a strong sense of smell that they use to their advantage.
- By detecting various scents in the soil, moles can locate food sources, such as earthworms, insects, and larvae.
- They can detect odors through their nostrils and their mouth, which they use to taste the air.
- Moles also use their sense of smell to identify potential predators or other moles that might compete for resources in their territory.
Hearing
- Although moles have poor hearing, they can detect low-frequency sounds and vibrations.
- This sense allows them to detect the movement of nearby prey or potential threats.
- Moles have adapted to rely mostly on their sense of touch and smell, but their hearing can also give them additional information about their environment.
Taste
- Moles have taste buds on their tongues, which they use to detect bitter and sweet flavors.
- They use their sense of taste to identify potential food sources and avoid toxic substances.
By combining these senses, moles create a comprehensive picture of their underground habitat. Their acute sense of touch, heightened sense of smell, limited hearing, and taste perception allow them to thrive in their subterranean world.
You May Also Like – Mouse in Bedroom Can’t Sleep? | 7 Powerful Solutions
Do All Moles Have Eyes?
While many species of moles have small eyes, some have evolved to live without them. Here are a few examples.
Do Golden Moles Have Eyes?
Golden moles, although not true moles, share similarities in their appearance and burrowing habits. These small, tailless insectivores consist of around 21 species.
Golden moles have non-functioning eyes that are vestigial and covered with skin. The optic nerve in these moles is reportedly degenerated. Instead of relying on vision, golden moles heavily depend on their sense of hearing to detect vibrations from predators and prey.
While they technically have eyes, they are non-functional and covered with skin, rendering them ineffective.
Do Star-Nosed Moles Have Eyes?
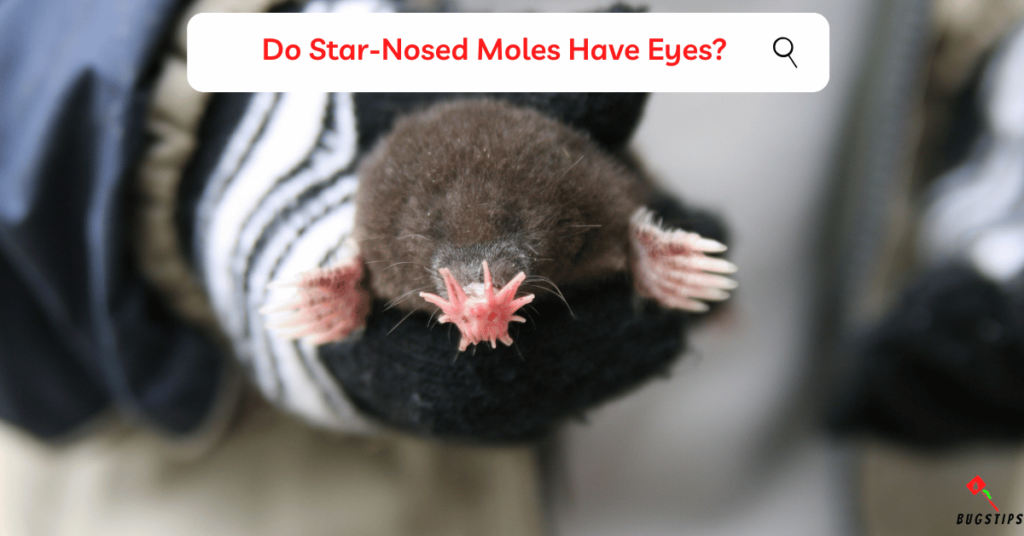

Star-nosed moles have eyes, but their visual capabilities are extremely limited. Their eyes are small and provide minimal visual input.
However, the star-nosed mole’s primary sense is touch. It utilizes the highly sensitive star-shaped appendages on its snout to explore its environment and locate food.
These appendages can detect prey in less than a quarter of a second. The star-nosed mole’s use of touch to understand its surroundings is analogous to how primates rely on their eyes.
While star-nosed moles have eyes, their reliance on touch surpasses their visual capabilities.
Do Ground Moles Have Eyes?

Ground moles, in general, have eyes, but their vision is not highly effective. Their eyes are often covered with fur or skin, which limits their visual acuity.
Additionally, the eyes of ground moles are not well-developed, further reducing their effectiveness in terms of vision.
These moles primarily rely on other senses, such as touch and smell, to navigate their underground habitats and locate food.
Do Russian Mole Rats Have Eyes?

Russian mole rats, specifically the species known as Spalax giganteus, do not have eyes at all.
These mole rats are completely blind, lacking both eye sockets and optic nerves. They have adapted to life in total darkness underground and they rely on their sense of touch and smell to navigate their underground tunnels and find food.
Why Do Moles Come Out at Night?
Moles are primarily active during the day and night, but they are more commonly seen above ground during the night. There are several reasons why moles prefer the cover of darkness.
- To Avoid Predators
- Moles have numerous natural predators, including birds of prey, foxes, and domestic pets.
- By being active at night, moles reduce their chances of encountering these potential threats.
- The darkness provides them with a veil of protection, allowing them to carry out their activities with reduced risk.
- To Evade Sunlight
- Moles are adapted to living in underground tunnels and prefer to avoid sunlight.
- Sunlight can be harmful to their sensitive eyes and skin.
- By primarily being active at night, moles can avoid the harsh glare of daylight.
Related Article – Skunk Smell in House at Night | The Truth
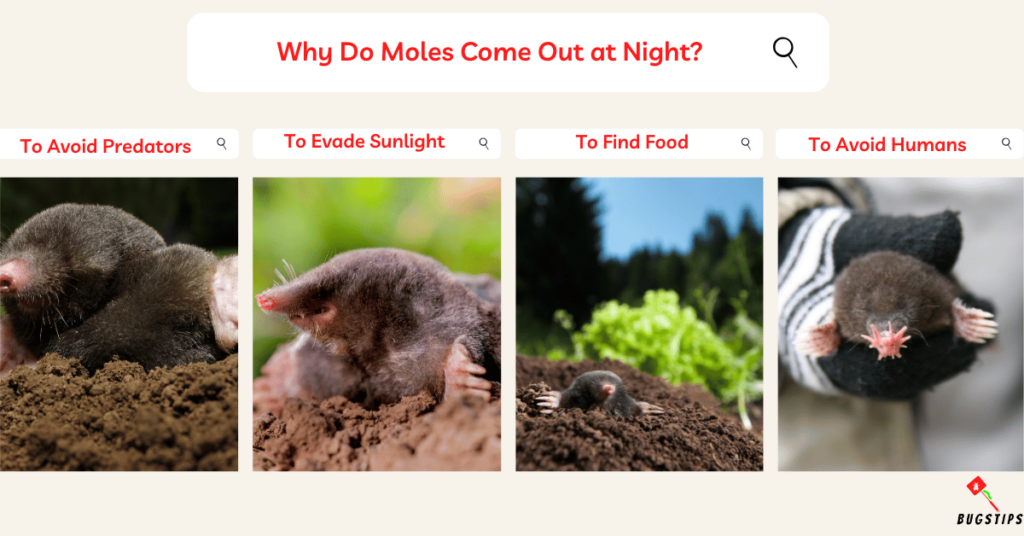
- To Find Food
- Moles primarily feed on earthworms, insects, and larvae that inhabit the soil.
- These food sources are more abundant and accessible during the nighttime.
- Earthworms, for example, tend to come closer to the surface at night, making it easier for moles to detect and capture them.
- By being active when their prey is most active, moles increase their chances of finding an ample food supply.
- For Optimal Temperature and Moisture
- Nocturnal activities provide moles with favorable environmental conditions.
- During the night, the soil temperature tends to be cooler, which helps prevent overheating.
- The soil is also typically more moist during the nighttime hours, facilitating easier digging and burrowing for moles.
- These conditions create a more comfortable and conducive environment for their underground lifestyle.
- For Reduced Human Interference
- Human activities, such as gardening, landscaping, and lawn maintenance, are more prevalent during daylight hours.
- By being primarily active at night, moles minimize the chances of encountering disruptions caused by human presence.
- his allows them to carry out their burrowing and foraging activities undisturbed.
Although moles are not strictly nocturnal animals, they are generally more active during quiet hours when there is less disturbance in their environment.
Final Thoughts
Moles are a fascinating group of animals with a wide range of vision capabilities. Some species have functional eyes, while others have adapted to living without them and rely on their other senses to survive.
Despite this variation, moles have developed highly acute senses of touch, smell, and hearing that allow them to navigate their underground habitats, locate food, and detect potential predators.
These adaptations have made moles highly effective in their subterranean environments, where they play important roles in their ecosystems.
Overall, whether they have functional eyes or not, moles are remarkable creatures that have developed unique sensory adaptations to thrive in their underground world.
FAQs
Can moles see colors?
Moles have limited color vision and perceive the world in shades of gray. They rely more on their other senses, such as touch and smell, for navigating their environment.
Are moles blind?
While not all moles are completely blind, some species, like the golden mole and Russian mole rat, are indeed blind. Other species may have small eyes that are not well-developed or functional.
Does moles’ eyesight deteriorate over time?
No specific evidence suggests that moles’ eyesight deteriorates with age. However, their eyes’ functionality may vary depending on factors such as health and environmental conditions.
How long do moles live?
Most mole species have relatively short lifespans, typically less than two years. However, some species, like Townsend’s mole, can live up to four to six years, depending on their environment and other factors.
Resources – (for further reading)
ScienceDirect – Mole senses
Encyclopedia Britannica – Mole | Burrowing Mammal, Adaptations & Behavior
The Mammal Society – Species – Mole